
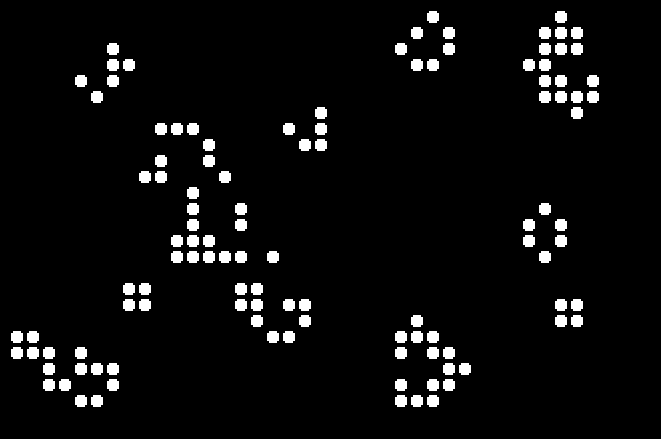
Well, as if most of the other stuff on this site isn't rather
odd.
I was only 7 when Conway's
Game
of Life was introduced in the pages of Scientific American
in October 1970, don't recall when I first heard about it but when
I got my first computer in 1981 (a ZX81 with a whopping 1K of ram
that I soldered together myself) it was one of the first programs
I wrote. First in BASIC but I wanted speed so rewrote it in Z80
machine code and was mesmerized by its fast-moving patterns! That
piece of code is long gone but I found a similar version of LIFE
that I wrote for the C64...

I don't have the assembly source for it, in those days I coded
the assembly on paper then converted the opcodes to the actual
bytes. Here's the original files, the
loader graphics to the left was made from three screen shots,
cropped and color-edited - the C64's default colors were rather
pale.
I coded versions of LIFE for every 8-bit computer I had, starting
with the ZX81, then the Tandy Color Computer, the C64 then the
Atari 800 and derivitives. Here's an animation made from my old
Atari CELLS program...

I fooled around with LIFE a bit in QBasic when I got a PC in 1993
but PC machine coding was nowhere near the fun of coding for
8-bitters and soon there were much better programs than anything I
could possibly come up with. LIFE is Turing-complete and it's
possible to craft a general-purpose computer in LIFE. Here's one
that runs Tetris. And one that runs LIFE in
LIFE. (!!! yikes !!!)
11/27/23 - Here's a version of LIFE written in Javascript... use the mouse
to change the cell states.
This is a strange one...

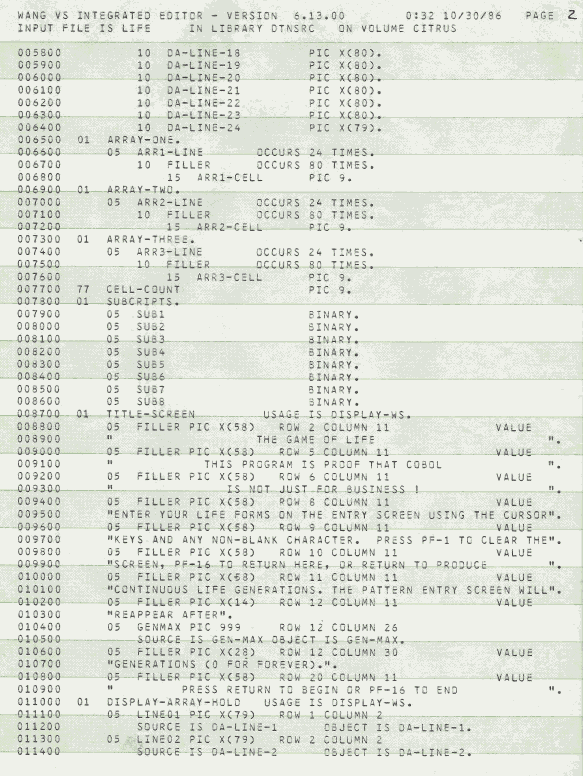
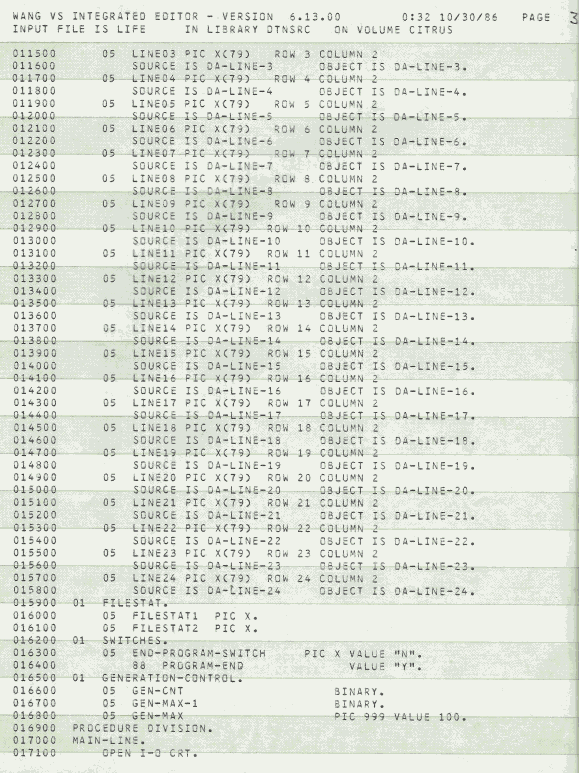


I wrote this when I had a gig as a night-time computer operator at Citrus World in 1986.. that's what happens when you teach a young computer geek COBOL then leave them alone with a mainframe. The Wang VS also had BASIC, played with it too but had to be careful as it did not multitask well and had a tendency to mess up the work jobs I was running. This COBOL version of LIFE didn't have a random mode (Wang VS COBOL didn't have a random number generator that I could tell), after entering a starting pattern it ran for a fixed number of cycles then I could keep going, clear the screen and enter a new pattern, or stop wasting time.
In the late '80's I worked at Shiloh Music in Mt. Juliet, TN and
we were an Atari dealer. Mostly for the Atari ST which was used by
many musicians back then, but also sold and serviced the Atari 800
line. I really liked the way the original 800 was made - like a
tank - but with only 48K was limited so ended up with an Atari XE
with 128K, the extra 64K could be configured as a ram disk but
eventually got another box with several hundred K of ram with
battery backup that I could trust better with my data. Atari DOS
was functional but mostly used SpartaDOS along with the Ace C
compiler and M65 assembler. The environment was primitive but
could edit, compile and link code that I wrote. The resulting
programs were extremely slow and low resolution by modern
computing standards but back then it was pretty much all I had to
work with. Here are some of the things I played with...
CELLS
This was a colorized version of LIFE, with different colors for
birth, survival by 2 and survival by 3. The original program
computed about one generation per second but it goes super-fast
when running under the Atari800 emulator in turbo mode.
HODGE
This is a 2D cellular automaton called the Hodgepodge Machine,
found in A.K. Dewdney's Computer Recreations column in the August
1988 issue of Scientific American. It was created by Martin
Gerhardt and Heike Schuster to simulate the waves that occur in
some kinds of chemical reactions. This implementation uses an 80
by 96 grid, each cell can have a number of states ranging from 0
for healthy and the maximum state for ill. Any state between the
two was termed infected. The multiple states are (somehow) reduced
to 4 colors for display.
The input variables are:
NS Number of cell states
K1 Constant 1 (infect)
K2 Constant 2 (ill)
G Rate of infection
For each generation the program makes the following computations
on each cell:
A = number of surr. infected cells
(currentstate>0 and <NS)
B = number of surr. ill cells
(currentstate = NS)
S = sum of surr. cell states
If currentstate=0 then newstate=[A/K1]+[B/K2]
If currentstate>0 and currentstate<NS then newstate=[S/A]+G
If currentstate=NS then newstate=0
...while keeping
track of the counts, after the future states of all the cells have
been computed then copies the new state to the current state,
displays and repeats. I forgot to press N for new when I took this
screen dump so it used the current memory contents as the starting
pattern...

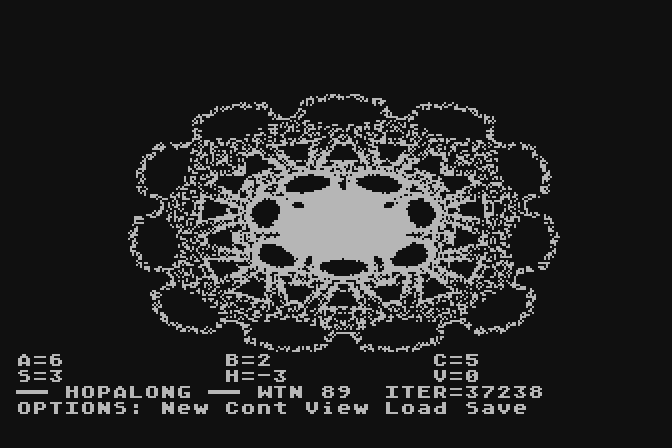
HOP
This is a version of the HOPALONG algorithm from Computer
Recreations, September 1986 Scientific American and also reprinted
in A.K. Dewdney's "THE ARMCHAIR UNIVERSE". I couldn't find the
source code for this particular program but this is the basic
algorithm, adapted from the article...
input a, b, c
x = 0
y = 0
clear screen
do
plot pixel x,y
x1 = y - sign(x) * sqrt(abs(b * x - c))
y = a - x
x = x1
until stopped
The S H and V parameters are the scaling factor and horizontal
and vertical position. Despite the imprecision of floating point
computer math (especially on an 8-bit computer) the "hop" tended
to avoid certain regions, leaving a pattern of voids...
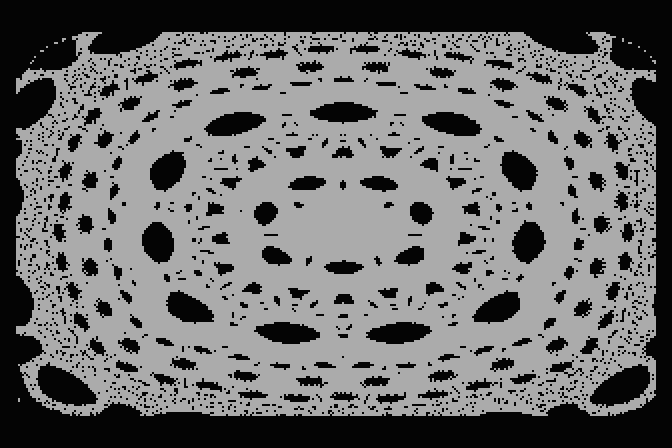
After many many more hops there are still voids...
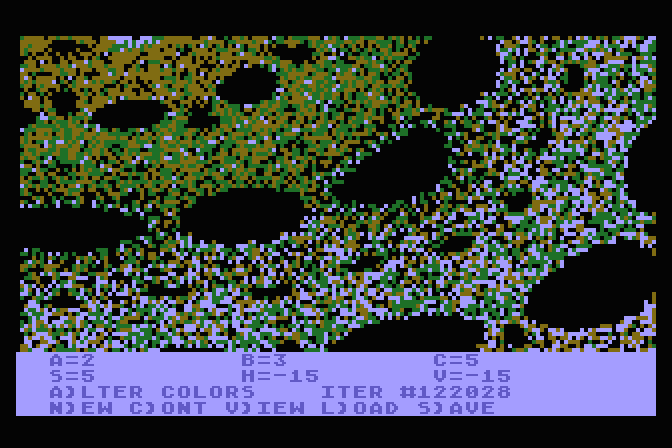
BURST
This is a color version of HOPALONG, using the iteration count to
periodically change the plotting color...
LNAUTO
This program generates various one-dimensional, or "line"
automata, using a user-entered rule string. Line automata have
been covered in the March and September 1984 issues of Scientific
American and in the December 1986 issue of Byte, and also heavily
researched by Stephen Wolfram. In this kind of automata the cell
influences its own outcome along with the states of its
surrounding cells. This program supports neighborhood sizes of 3,
5 or 7, determined by the length of the rule string, and up to 4
states numbered 0-3. To compute the next state of each cell the
program adds up the states of all the cells in the neighborhood
then looks up the appropriate digit in the rule string, with the
left-most digit specifying the new state for a count of 0. When
successive generations are plotted from top to bottom interesting
patterns emerge...

MORPH
This program plots "Biomorphs", invented when IBM researcher
Clifford Pickover had a bug in a fractal program that produced
unexpected results, and reported by A.K. Dewdney in the July 1989
issue of Scientific American. The idea is for each pixel iterate
Z=something(Z)+C with Z and C being complex numbers. C is held
constant to determine the type of plot and the real and imaginary
components of starting value of Z are swept to generate a 2D plot.
Something(Z) can be any function of Z, from simple to complex. In
my version I use one of 4 formulas from Z=Z^2+C to Z=Z^5+C. Each
pixel is iterated until the absolute size of Z exceeds a limit or
an iteration limit is reached. For my plots if both components of
Z are less than the limit that point is plotted with color 0,
color 1 if only the real component is less than the limit, color 2
if only the imaginary component is less than the limit, or color 3
if both components exceed the limit. There's something in there...
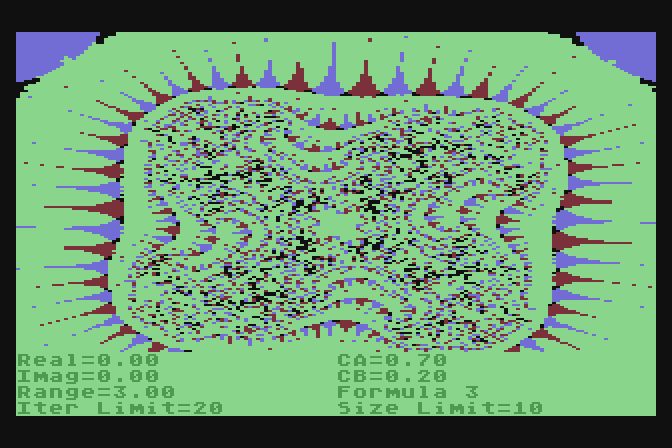
SCOPE
This is a Mandelbrot
Set plotter. It produced interesting images for the day...
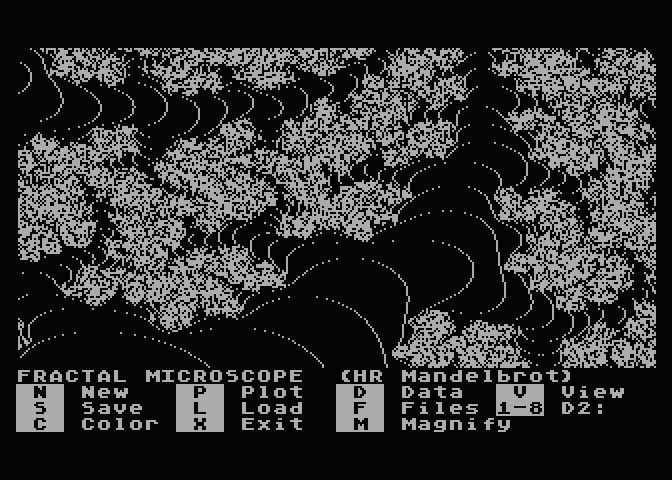
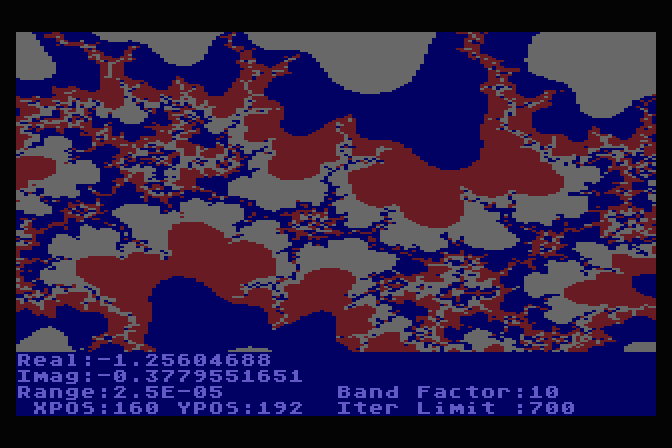
...but was infuratingly slow! Many hours per plot on the original
Atari computer. Even with the Atari800 emulator's super-fast turbo
mode it still takes several minutes per image. Back then I'd still
run it overnight to see what would come out, and wonder how such
images appear in otherwise ordinary numbers processed by
relatively simple math.. as if Nature is an artist! When I got a
PC in 1993 it wasn't too long thereafter when I discovered
FractInt and many other fractal programs, each generation
exponentially increasing in speed. These days the Mandelbrot set
can be zoomed into in real time using software such as XaoS, but it still
takes a lot of computing for an extreme zoom. Here are some things I found around 8 years ago using
a program called Fraqtive,
they make nice desktop wallpaper.
TREK
I played with more than math... had many games back then but this
was one of my favorites...
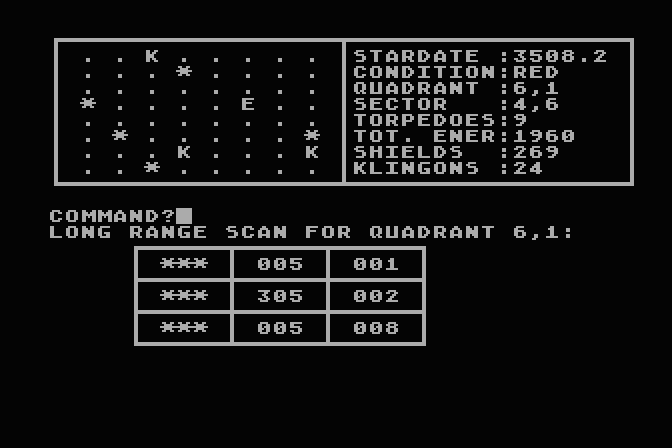
This version of Mike
Mayfield's TREK game is based on "Super Star Trek",
published by David Ahl in 1978 in his book "BASIC Computer Games,
Microcomputer Edition". I typed it in and converted it to Atari
BASIC sometime around 1990. I remember playing it quite a bit but
the code I found still had several cosmetic glitches - not sure if
this was an early conversion (some things hadn't been converted at
all) or if I just didn't care at the time - the game logic worked
fine. The main conversion was to keep the main screen at the top
so I wouldn't have to keep typing SRS all the time (plus it looked
cool), then display temporary data on the bottom half of the
screen. Which mostly worked but got tricky when firing at a bunch
of Klingons then they'd shoot back, overwriting the previous text
and sometimes leaving a messy display. Or worse scrolling the top
display. Most of the recent fixes involved adding space padding to
keep things neat and making sure the top display is properly
updated. In most versions of this game the enemy ships fired first
when entering a new quadrant. This one didn't do that and also
seemed a bit on the easy side, so added a difficulty level prompt
when the program starts. Level 0 keeps the easy gameplay, higher
levels strengthen the enemies and increase the chance they'll
shoot first.
Update Febuary 2021 - At it again.. recently I got back into Trek
hacking and sure enough found a few more display glitches in this
version where it would overwrite existing text without clearing it
first, or in the case of technicians fixing my ship, completely
obliterating the SRS display - bad techs! Can't have that.. fixed
that and other glitches, should be better now but there are likely
other bugs. One bug that I know of is on the new higher levels,
sometimes SRS will trigger another round of incoming fire -
normally SRS isn't needed as its mostly automatic in this version,
except for when the display glitches.
Download the maprogs.zip file for disk images containing all of these programs plus scripts for running with the Atari800 emulator (last updated 2/22/2021). The disk images also work with other Atari emulators such as Altirra for Windows. Or browse through the converted source code and text.
This is fun program...
-------------- begin lineauto.bas ------------------
REM LineAuto - WTN 231203-12 - FreeBASIC version, -lang qb -exx REM Generates line automata with up to 10 states, 3 cell neighborhood REM For each cell the next state is determined by the sum of states REM in the neighborhood and the rule string which specifies the next REM state for every possible sum. The rule string starts at sum 0 and REM can be up to 28 digits long. ON ERROR GOTO ProgError RANDOMIZE 'TIMER 'uncomment timer for QBasic DEFINT A-Y 'start floating point vars with z scmode = 18 'for QBasic make 12 (disables S key) 'otherwise 18=640x480 19=800x600 20=1024x768 21=1280x1024 xres = 1280 'for dimensioning arrays, make 640 for QBasic DIM rule(28), oldstate(xres), newstate(xres) startline = 16 'must be even magnify = 0 'in magnify mode the middle is printed with double sized pixels historysize = 1000 'divisible by 4, for QBasic have to greatly reduce (24) DIM history(28, historysize) 'rule history for back DIM historystart(xres, historysize) 'saved starting lines for back feature DIM previous(xres, historysize) 'saved starting lines for previous feature hp = 0: bp = 0: nrf = 0 'history pointer, back pointer, new rule flag maxhp = 0 'highest saved history rule Xclose$ = CHR$(0) + "k" 'code for window close CursorLeft$ = CHR$(0) + "K" 'code for cursor left CursorRight$ = CHR$(0) + "M" 'code for cursor right GOSUB SetScreenMode resetfactors: CLS znfactor = 3.7 'used to weight random rule digits lower zsfactor = 0.4 'used to weight random rule states higher zxfactor = 0.7 'used to weight random rule digits higher for higher sums PRINT "*** LineAuto *** by WTN 231203-12" PRINT PRINT "This program generates line automata graphics with up to 10 states" PRINT "per cell. Generation starts with a random line, for each new line" PRINT "the cell states are determined by summing the 3 cells above it then" PRINT "getting the next state from the rule string. The rule string starts" PRINT "with the state for a sum of zero. The line wraps at the edges." PRINT "Press a key within 3 seconds to pause this screen." PRINT PRINT "Edit mode keys..." PRINT "Left/Right move green cursor" PRINT "0 through 9 change rule digit" PRINT "Enter generate using current rule" PRINT "N generate from new random rule" PRINT "C clear rule string to zeros" PRINT "M toggle magnify mode" PRINT "S change screen size" PRINT "X exit the program" PRINT PRINT "After generating..." PRINT "Space generate next screen" PRINT "Esc back to edit mode" PRINT "P regenerate previous screen" PRINT "N generate from new random rule" PRINT "B go back through rule history" PRINT "F go forward in rule history" PRINT "X exit the program" PRINT: i = 3 'seconds to wait stwait1: SLEEP 1: a$ = INKEY$: IF a$ <> "" THEN GOTO stwait2 i = i - 1: IF i > 0 THEN GOTO stwait1 ELSE GOTO ClearScreen stwait2: PRINT "(press W for weights or any key to continue)" SLEEP: a$ = INKEY$: IF a$ = Xclose$ THEN SYSTEM IF a$ <> "w" THEN GOTO ClearScreen CLS PRINT "Weights when making new random rules, must be > 0" PRINT "1=no weight, < 1 weights higher, > 1 weights lower" PRINT "znfactor weights digit selections, generally lower" PRINT "zsfactor weights number of states, generally higher" PRINT "zxfactor weights digits towards the end, generally higher" PRINT PRINT "Enter znfactor, currently"; znfactor; INPUT ": ", znfactor: IF znfactor <= 0 THEN GOTO resetfactors PRINT "Enter zsfactor, currently"; zsfactor; INPUT ": ", zsfactor: IF zsfactor <= 0 THEN GOTO resetfactors PRINT "Enter zxfactor, currently"; zxfactor; INPUT ": ", zxfactor: IF zxfactor <= 0 THEN GOTO resetfactors ClearScreen: CLS : PRINT "*** LineAuto *** "; EnterRule: LOCATE 1, 18: PRINT "X-exit Enter-go NewClrMS Rule: "; LOCATE 1, 79: IF magnify = 0 THEN PRINT " "; ELSE PRINT "M"; nrf = 0: rp = 48: dp = 1: GOSUB ShowRule entry1: a$ = INKEY$: IF a$ <> "" THEN GOTO entry1 LOCATE 1, dp + rp: COLOR 2: PRINT CHR$(rule(dp) + rp); LOCATE 1, dp + rp: SLEEP 1: a$ = INKEY$: GOSUB RndStuff IF a$ = "" THEN GOTO entry1 IF a$ = "c" THEN GOSUB ResetColor FOR i = 1 TO 28: rule(i) = 0: NEXT i: GOTO EnterRule END IF IF a$ = "m" THEN GOSUB ResetColor IF magnify = 0 THEN magnify = 1 ELSE magnify = 0 GOTO ClearScreen END IF IF a$ = "x" OR a$ = Xclose$ THEN GOTO ExitProgram IF a$ = CHR$(13) THEN GOSUB ResetColor: GOTO DoAutomata IF a$ = CursorLeft$ THEN IF dp > 1 THEN GOSUB ResetColor: dp = dp - 1 GOTO entry1 END IF IF a$ = CursorRight$ THEN IF dp < 28 THEN GOSUB ResetColor: dp = dp + 1 GOTO entry1 END IF IF a$ = "n" THEN GOSUB ResetColor: GOTO RandomRule IF a$ = "s" AND scmode > 17 THEN 'change screen size scmode = scmode + 1: IF scmode > 21 THEN scmode = 18 GOSUB SetScreenMode: GOTO ClearScreen END IF IF LEN(a$) > 1 THEN GOTO entry1 IF a$ < "0" OR a$ > "9" THEN GOTO entry1 GOSUB ResetColor: PRINT a$; : rule(dp) = VAL(a$): nrf = 1 IF dp < 28 THEN dp = dp + 1 GOSUB ShowRule: GOTO entry1 SetScreenMode: SCREEN scmode IF scmode = 12 OR scmode = 18 THEN xres = 640: yres = 480 IF scmode = 19 THEN xres = 800: yres = 600 IF scmode = 20 THEN xres = 1024: yres = 768 IF scmode = 21 THEN xres = 1280: yres = 1024 RETURN ResetColor: COLOR 15: PRINT CHR$(rule(dp) + rp): LOCATE 1, dp + rp RETURN ShowRule: REM determine the biggest digit in the rule, cursor pos in dp maxdigit = 0 FOR i = 1 TO 28 IF rule(i) > maxdigit THEN maxdigit = rule(i) NEXT i rulesize = maxdigit * 3 + 1 IF rulesize < 4 THEN rulesize = 4 'not less than 4 REM print the rule, suppressing unreachable digits after cursor LOCATE 1, rp + 1 FOR i = 1 TO 28 IF i > rulesize AND i > dp THEN PRINT " "; ELSE PRINT CHR$(rule(i) + 48); NEXT i RETURN RandomRule: FOR i = 1 TO 28: rule(i) = 0: NEXT i 'zero previous rule nstates = INT(RND(1) ^ zsfactor * 9 + 2) '2 to 10 states znf2 = (znfactor * nstates) / 10 'adjust znfactor for number of states okflag = 0: IF znf2 < 1 THEN znf2 = 1 'minimum no weighting rulesize = (nstates - 1) * 3 + 1 FOR i = 1 TO rulesize 'weight lower with znf2, then higher for later digits rint = INT((RND(1) ^ znf2) ^ (zxfactor ^ (i / rulesize)) * nstates) rule(i) = rint: IF rint = nstates - 1 THEN okflag = 1 'ensure at least 1 max NEXT i: IF okflag = 0 THEN GOTO RandomRule 'do again if bad rule nrf = 1 'new rule DoAutomata: dp = 1: LOCATE 1, 18: PRINT "X-exit Spc-next EscPNBF "; : pkey = 39 GOSUB ShowRule 'also calculates maxdigit used below IF maxdigit = 0 THEN GOTO EnterRule REM initialize line to random states from 0 to maxdigit FOR i = 1 TO xres: newstate(i) = INT(RND(1) * (maxdigit + 1)): NEXT i ln = startline: GOSUB DrawLine 'increments ln by 1 or 2 if magnified IF nrf <> 0 THEN 'new rule, copy to history hp = hp + 1: IF hp > historysize THEN hp = 1 FOR i = 1 TO 28: history(i, hp) = rule(i): NEXT i 'save rule FOR i = 1 TO xres: historystart(i, hp) = newstate(i): NEXT i 'save start bp = hp 'set back pointer to current history ptr IF hp > maxhp THEN maxhp = hp 'highest saved history END IF: pp = 0 'clear previous starting pattern history Generate: IF pp < historysize THEN 'save starting pattern to allow previous pp = pp + 1: FOR i = 1 TO xres: previous(i, pp) = newstate(i): NEXT i ELSE 'save last fourth of history and reset pp to 3/4 LOCATE 1, pkeY: COLOR 4: PRINT "P"; : COLOR 15 'turn the P reminder red p5 = historysize / 2: p75 = historysize / 4 + p5 FOR j = historysize TO p75 STEP -1 FOR i = 1 TO xres: previous(i, j - p5) = previous(i, j): NEXT i NEXT j: pp = p75 GOTO Generate END IF __ScreenLock() 'prevents screen updates until unlock, comment for QBasic autoloop: REM copy newstate array to oldstate FOR i = 1 TO xres: oldstate(i) = newstate(i): NEXT i REM loop for each cell FOR i = 1 TO xres REM count the states in the neighborhood sum = 0 FOR j = i - 1 TO i + 1 k = j IF k < 1 THEN k = k + xres IF k > xres THEN k = k - xres sum = sum + oldstate(k) NEXT j REM use the count to get the next state from the rule array newstate(i) = rule(sum + 1) NEXT i GOSUB DrawLine IF INKEY$ = CHR$(27) THEN __ScreenUnLock() 'comment for QBasic GOTO EnterRule END IF IF ln < yres THEN GOTO autoloop __ScreenUnlock() 'comment for QBasic waitloop: IF INKEY$ <> "" THEN GOTO waitloop SLEEP 1: a$ = INKEY$: GOSUB RndStuff IF a$ = "" THEN GOTO waitloop IF a$ = "n" THEN GOTO RandomRule IF a$ = "b" THEN GOTO GoBack IF a$ = "f" THEN GOTO GoForward IF a$ = " " THEN ln = startline: GOTO Generate IF a$ = "x" OR a$ = Xclose$ THEN GOTO ExitProgram IF a$ = CHR$(27) THEN GOTO EnterRule IF a$ = "p" AND pp > 1 THEN 'go back to previous start pp = pp - 1: FOR i = 1 TO xres: newstate(i) = previous(i, pp) NEXT i: pp = pp - 1: ln = startline: GOTO Generate END IF GOTO waitloop GoBack: bp = bp - 1 IF bp < 1 THEN bp = maxhp RestoreRule: FOR i = 1 TO 28: rule(i) = history(i, bp): NEXT i 'restore rule FOR i = 1 TO xres: newstate(i) = historystart(i, bp): NEXT i 'restore start ln = startline: pp = 0: nrf = 0 'reset pointers, clear new rule flag GOSUB ShowRule: GOSUB DrawLine: GOTO Generate GoForward: bp = bp + 1 IF bp > maxhp THEN bp = 1 GOTO RestoreRule DrawLine: IF magnify = 0 THEN FOR p = 1 TO xres PSET (p - 1, ln), newstate(p) NEXT p ln = ln + 1 ELSE 'plot only half the line using 4 pixels per cell FOR p = 1 TO xres / 2 c = newstate(p) PSET (p * 2 - 2, ln), c PSET (p * 2 - 2, ln + 1), c PSET (p * 2 - 1, ln), c PSET (p * 2 - 1, ln + 1), c NEXT p ln = ln + 2 END IF RETURN RndStuff: 'called once a second while waiting for keypress z = RND(1) IF z < 0.01 THEN 'probably remove this block for QBasic FOR myi = 1 TO xres: FOR myj = 0 TO newstate(myi) 'loop through line z = RND(1): NEXT myj: NEXT myi 'calling rnd state times to scramble rng END IF RETURN ProgError: __ScreenUnlock() 'comment for QBasic LOCATE 1,1: PRINT "Error";ERR;"at line";ERL; " press E to exit "; errorwait: IF INKEY$ <> "e" THEN GOTO errorwait ExitProgram: SCREEN 0: SYSTEM -------------- end lineauto.bas --------------------
When compiled with FreeBASIC and executed it
produces images like these... (screen dumps from an earlier
version)
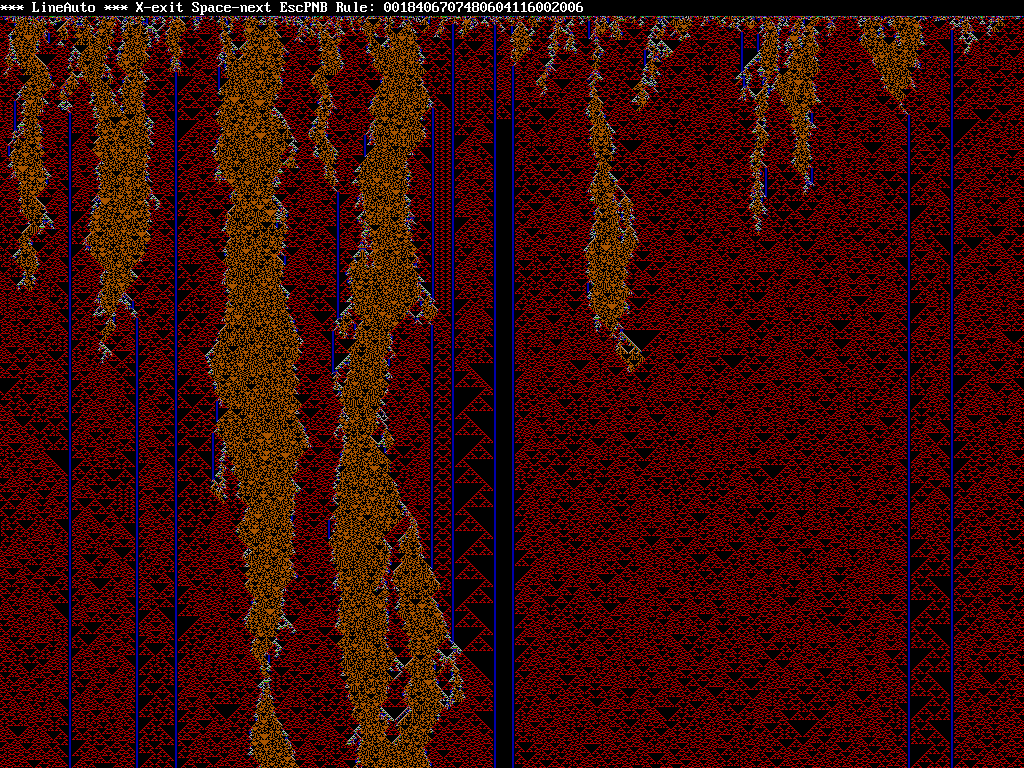
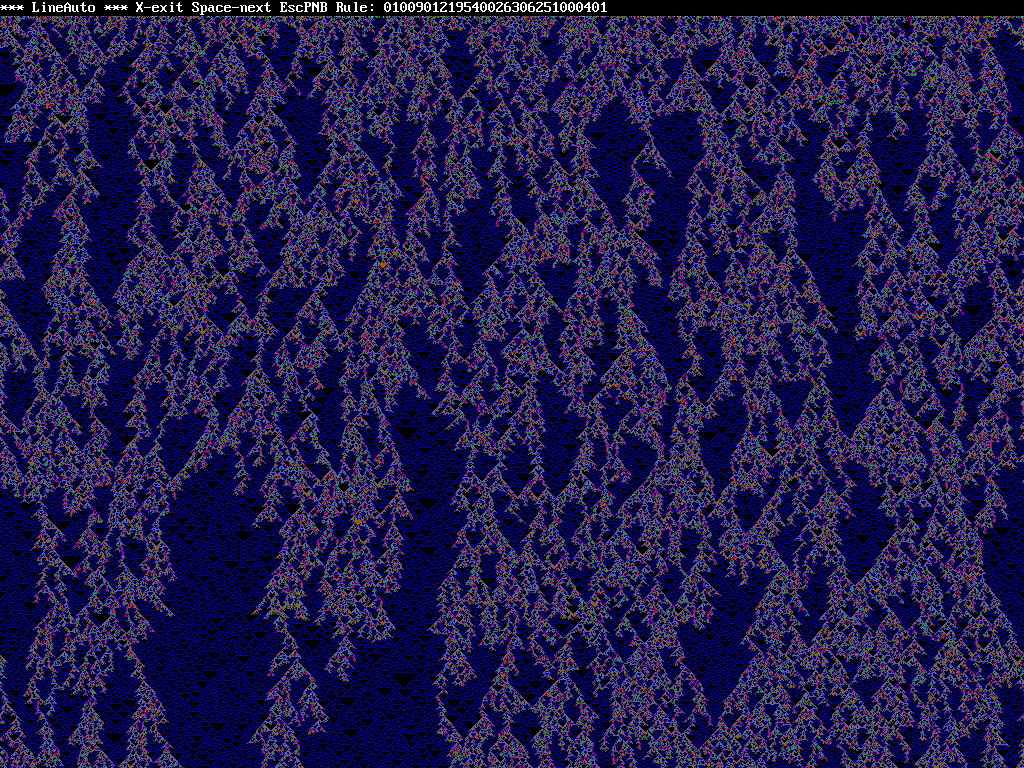
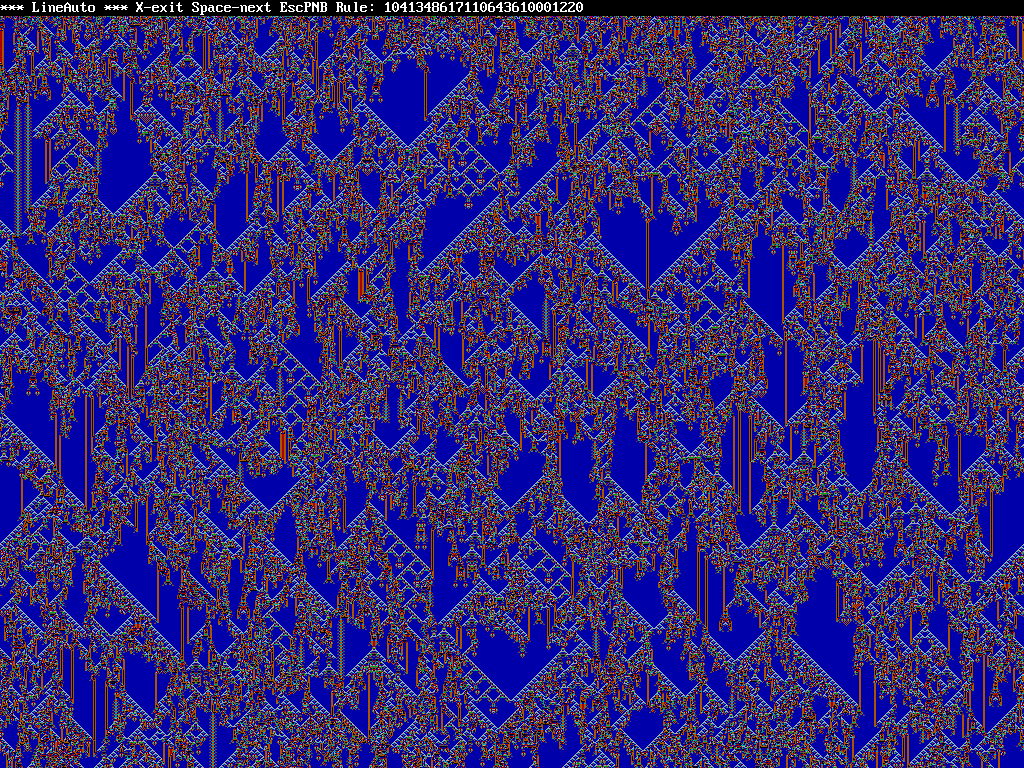
I've dabbled with line automata generators pretty much ever since
I had computers but they were limited to only 4 states since they
only had 4 colors in "high" resolution mode. My inspirations for
these back in the day usually came from the Computer Recreations
column in Scientific American (see LNAUTO references above),
however recently I've been reading "A New Kind Of
Science" by Stephen Wolfram and all the pretty pictures got
me thinking again. In the book many of the automata are fully
specified using his "rule" system where all possible combinations
of surrounding cells are specified, but this gets unwieldy fast
when there are more than a few states - for the 10-state automata
generator above fully specifying the next state would require a
1000 digit rule string to specify the next state for previous
states 000 to 999. Rather this lineauto program does what I have
always done and considers only the sum of states in the 3 cell
neighborhood, this method only requires a 28 digit rule for 10
states. Despite not being fully specified (or for that matter
hardly at all, the cell's previous state is just another
summation) the patterns it produces are very similar to the
original research, but with more color. This method is termed
"totalistic", a description of the method is in this reposting
of the May 1985 Computer Recreations column. My technique is
pretty much the same except I specify the rule string backwards,
starting with the next state for a sum of 0. This program is
compatible with the rule strings from LNAUTO and other line
automata programs I've made, but now the digits can range from 0-9
rather than being limited to 0-3.
Here's a QBasic-style program that converts the totalistic codes
from the NKS book into the lineauto rule string format...
'convert 1D automata codes from NKS to lineauto format digits$ = "0123456789" again: INPUT "Enter number of states (typ 3 or 4): ", ns% IF ns% < 2 OR ns% > 10 THEN SYSTEM INPUT "Enter NKS code to convert: ", code& result$ = "" calcresult: result$ = MID$(digits$, (code& MOD ns%) + 1, 1) + result$ code& = code& \ ns%: IF code& > 0 THEN GOTO calcresult PRINT "Equivalent lineauto rule = "; FOR i = LEN(result$) TO 1 STEP -1 'reverse the output PRINT MID$(result$, i, 1); NEXT i PRINT : GOTO again
...or use any number base converter, just reverse the converted
number string when entering into lineauto as it starts with digit
0.
Here's a zip
package (179K version 231203-12) containing the lineauto
source code, docs and binaries for Windows and Linux. The Windows
is 32-bit, worked on my VirtualBox Windows 7 and 10 installs. The
Linux binary is 64-bit to match the vast majority of systems, it
has dependencies - libX11 stuff, libtinfo libpthread etc - but
worked on a fresh Ubuntu 23.10 without having to install anything.
11/21/23 - Ok took a couple days to stabilize but I think the
lineauto program is doing pretty close to what I want it to do.
The basics have always worked fine since the initial posting on
11/19/23, which was suppost to be to make me stick a fork in it
but of course that never seems to happen, but it did have the
effect of locking in the basic concept so that I wouldn't tinker
with it too much. The tweaks and updates come from playing with
the program, fixing things as I go. Things like locking the screen
while updating to avoid screen flicker, which had the side effect
of making it much faster and making be run past interesting
patterns, so added rule and pattern history buffers to go back to
what I missed.
The other thing I was trying to figure out how best to randomly
generate rules that resulted in less noise and more good stuff.
With a rule string of 28 digits each 0-9 there are more than a
trillion trillion possible combinations, but the random number
generator has a 24 bit seed, so at best can output only about 4
million possible sequences so first step was adding additional
randomness by making extra calls to RND based on time at the
prompt and using the obvious internal source of entropy - the
automata states - to further perturb the random generator. This
should make it at least possible to generate a given rule string
(the universe might end before it lands on it, but being
theoretically possible is better than numerically impossible).
Simply randomly generating rule digits doesn't work so well, as
can be tested by running the program and pressing a key to pause
the intro screen then pressing W to set the weights all to 1 to
evenly distribute the digits. Pressing N repeatedly produces a few
interesting patterns but most of the rules just generate noise.
The trick is to weight the digit selection to tend towards smaller
digits and zero, more so when there are more states. Another
optimization I am experimenting with is weighting the rule string
digits for higher sums towards higher values, possibly canceling
out the weighting towards smaller digits, so that higher digits
tend to occupy higher sum positions and extra pattern generators
can live up there, I call these "gadgets". What I am noticing with
10 states is that makes the rule big enough that multiple types of
patterns can coexist at the same time. Simpler 4 state automata
did that too but it can do more of that when there are up to 10
states. The scheme I have now seems to work fairly well - it
doesn't take very many N presses to produce cool pictures that
likely have never been seen before - but I'm sure the weighting
can be improved. I'm still trying to get a feel for trying to
predict what a given rule digit distribution will do. Fortunately
many different rules will produce similar or even exactly the same
patterns, it doesn't have to hit it spot on. Sometimes with
interesting rules I'll zero out rule digits one at a time to find
the ones that have little or no effect. Sometimes seemingly simple
rules exibit surprisingly complex behavior, check out rule string
000340000000...
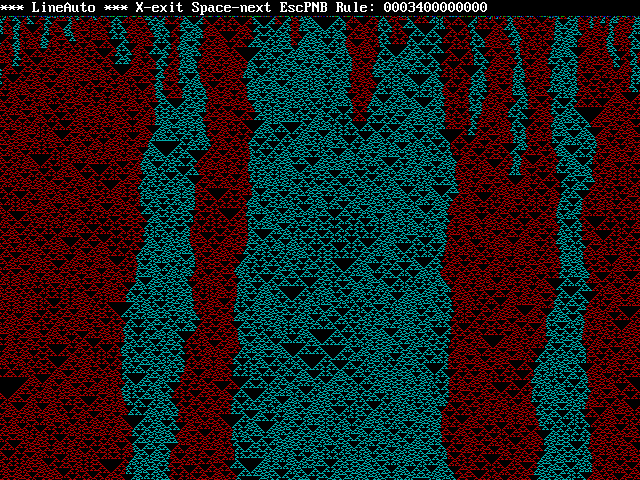
...in this case blue "won" but about half the time the red
triangles take over. Note that the 3 is in the sum 3 position and
the 4 is in the sum 4 position. So what happens if I add a 5 in
the 5 position? You guessed it...
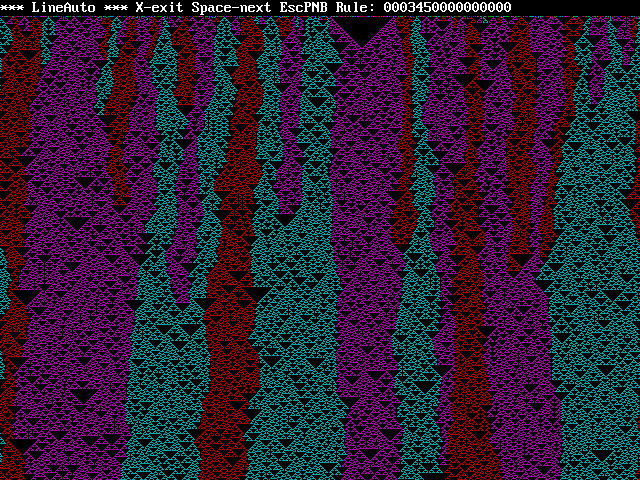
2 and 6 didn't work but 7 did...
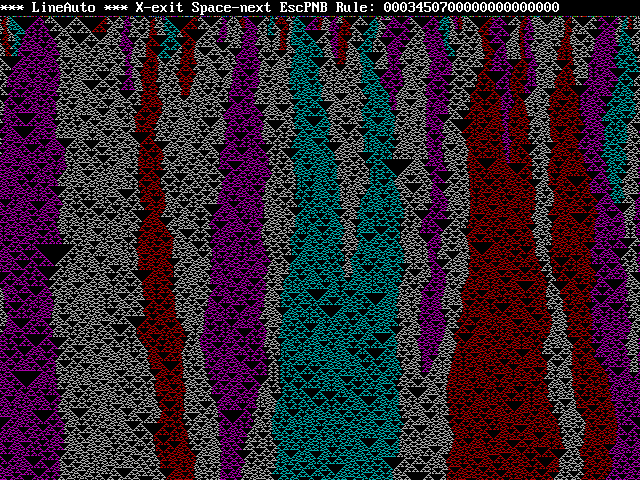
Let's add a gadget higher in the rule string...

...I so don't understand what's going on here, it's like peering
into the brain of an alien computer (or nature).
11/22/23 - One thing that was bothering me was the Back feature
to restore the previous rule didn't restore the starting pattern
so even though it was the same general pattern the image was
different. Now it saves and restores the starting pattern too.
11/27/23 - Here's a version of LineAuto written in Javascript...
The TRS-80 Color Computer and a program to
dump CAS files
11/11/24
This was my second computer after the ZX81 (which I soldered
together), it was my first serious 8-bit computer - the ZX81
taught me things like machine code and programming but it left a
lot to be desired.. like a real keyboard and memory that didn't
crash the machine if touched it. I can't remember the exact year
but guessing it was around 1983 when I got my CoCo with a cassette
deck.. I think it was a version 2 but not sure. Not sure what
happened to it.. in my "archives" (the back room) I still have at
least the PCB from the ZX81 but the CoCo got lost somewhere along
the way. It was a funny time in my life - I knew electronics and
worked at a consumer electronics service center fixing stereos and
VCR's but I wanted more, so flew down south and... learned COBOL..
ugh but in a perverse kind of way I kind of liked it (see above
for my COBOL version of Conway's Game Of Life). At least it was
better than RPG - I absolutely hated that "language" (I don't
think RPG even deserves that title). But the CoCo got lost along
the way, only got to play with it for a year or less but it was a
very cool computer. And yes I like 6809 machine code better than
6502 but either one is better than Z-80 or anything more modern.
Fast forward ~40 years then a few days ago John Metcalf emailed
me to tell me about his upcoming CoreWar
tournament and he was also accepting entries for Color Robot
Battle, a game for the CoCo released back in 1983. Hole meet
rabbit. Too late for me to put together an entry - so far John's
Tau robot kicks the ass out of everything I've come up with so
far, maybe next year. But wow, what a blast from the past. I
missed this program back in the day (and it was $40 for the
cartridge, that was a lotta bank back then) but thanks to the
internet and people who care I found a copy of the cart and an
emulator to run it on (David Keil's DMK CoCo2 version 2.10
downloaded from CoCo Central). It's actually
a DOS program (I run it using DosBox) but it works better for me
than VCC - VCC is very nice but the status bar flickers like crazy
when running in wine on my Linux Ubuntu system - other than the
flickering VCC works great and I'd use it if running Windows. The
dos program is limited to 8.3 filenames but whatever I'm used to
that. The Color Computer Archive
also has these emulators along with tons of other stuff..
including the Color Robot Battle program. An archived copy of an
older version of the DMK dos emulator and its documentation may
be here.
Much of the software is in ".CAS" (cassette) format, including
the CRB robots. It's non-encoded so a hex dump will show the raw
text but it would be lots nicer to see it properly formatted, so I
wrote a QBasic program to help me with that...
---------------------- begin convcas.bas -----------------------------------------
REM CONVCAS,BAS 241111 WTN - for QBASIC or FreeBasic (fbc -lang qb -exx) REM converts TRS-80 COCO CAS files to text files REM Originally made to dump Color Robot Battle robots to text files, REM extended to also dump BASIC and machine code programs (must have header). REM For BASIC, detokenizes (using the info I found), unprintable chars REM will be output as [HH] where HH = hex value. For CODE or if format is REM BINARY, outputs a hex dump with addresses starting at the load address. REM For non-binary DATA or if no header, outputs only printable characters REM to the output file. CR will be converted to line end (LF or CRLF). REM CAS file format summary... REM Leader of 0x55 bytes possibly with 0x00 bytes in between REM Sync byte 0x3C - if not found says no sync and stops converting REM Block type byte - 0x00 = name block, 0x01 = data block, 0xFF = EOF block REM Block length byte (00-FF) REM 0 to 255 data bytes REM Checksum byte - block type plus length byte plus all data bytes MOD 255 REM Trailing 0x55 byte REM Repeat for all blocks on the tape REM Name block must have a length of 15 bytes... REM 8 bytes for program name padded with zeroes REM File type byte - 0x00 = BASIC, 0x01 = DATA, 0x02 = CODE REM Format flag byte - 0x00 = ASCII, 0xFF = BINARY REM Gap flag byte - 0x01 = continuous, 0xFF = gaps (ignored) REM Two bytes for start address (CODE only, otherwise 0000) REM Two bytes for load address (CODE only, otherwise 0000) REM EOF blocks have a length of 0 and no data bytes. REM Something like that. This parser is rather lax, checksum is ignored, REM trailing 55 isn't enforced (just loops back to the next leader), and REM block leaders can be any combination of 00 or 55, parses until 3C REM received or EOF. Truncated/damaged files can cause a program error. start: debug = 1 '0 = normal 1 = output hex to console 2 = force hex dump in output ON ERROR GOTO badfilename INPUT "CAS file to convert: ", infile$ infile$ = LTRIM$(RTRIM$(infile$)) IF infile$ = "" THEN SYSTEM IF UCASE$(RIGHT$(infile$, 4)) = ".TXT" THEN PRINT "CAS file cannot have .TXT extension": GOTO start END IF OPEN infile$ FOR INPUT AS #1 CLOSE #1 OPEN infile$ FOR BINARY AS #1 ON ERROR GOTO progerr p = INSTR(infile$, ".") IF p = 0 THEN p = LEN(infile$) + 1 outfile$ = LEFT$(infile$, p - 1) + ".txt" PRINT "Converting "; infile$; " to "; outfile$ OPEN outfile$ FOR OUTPUT AS #2 odd = 0 state = 0 binarycode = 0 'set to 1 to output binary detokenize = 0 'set to 1 to detokenize (only asks once) basicfile = 0 'set to 1 if basic file (resets per file) basicstate = 0 'keep track of detokenizing process (see sub) linenumber = 0 loadaddress = 0 WHILE NOT EOF(1) GOSUB getbyte IF state = 0 THEN IF byte = 0 THEN GOTO nextbyte IF byte = &H55 THEN GOTO nextbyte IF byte = &H3C THEN state = 1: GOTO nextbyte PRINT "No sync": GOTO endprog END IF IF state = 1 THEN IF byte = 0 THEN state = 2: GOTO nextbyte IF byte = 1 THEN state = 3: GOTO nextbyte IF byte = &HFF THEN state = 4: GOTO nextbyte END IF IF state = 2 THEN basicfile = 0: basicstate = 0: binarycode = 0: loadaddress = 0 PRINT "reading name block, length ="; byte IF byte <> 15 THEN PRINT "invalid name block length": GOTO endprog PRINT #2, "" PRINT #2, "******************************************************" PRINT #2, "NAME:"; IF debug THEN PRINT "NAME:"; FOR i = 1 TO 8 GOSUB getbyte IF byte = 0 THEN PRINT #2, " "; : ELSE PRINT #2, CHR$(byte); IF debug THEN IF byte = 0 THEN PRINT " "; : ELSE PRINT CHR$(byte); NEXT i PRINT #2, " TYPE:"; : IF debug THEN PRINT " TYPE:"; GOSUB getbyte IF byte = 0 THEN basicfile = 1: detokenize = 1 PRINT #2, "BASIC"; : IF debug THEN PRINT "BASIC"; END IF IF byte = 1 THEN PRINT #2, "DATA "; : IF debug THEN PRINT "DATA "; IF byte = 2 THEN PRINT #2, "CODE "; : binarycode = 1: IF debug THEN PRINT "CODE "; END IF PRINT #2, " FORMAT:"; : IF debug THEN PRINT " FORMAT:"; GOSUB getbyte IF byte = 0 THEN PRINT #2, "ASCII "; : IF debug THEN PRINT "ASCII "; IF byte = 255 THEN PRINT #2, "BINARY"; : binarycode = 1: IF debug THEN PRINT "BINARY"; END IF GOSUB getbyte 'ignore gap PRINT #2, " SA/LA:"; : IF debug THEN PRINT " SA/LA:"; GOSUB getbyte: PRINT #2, RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); IF debug THEN PRINT RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); GOSUB getbyte: PRINT #2, RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); " "; IF debug THEN PRINT RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); " "; GOSUB getbyte: PRINT #2, RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); IF debug THEN PRINT RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); loadaddress = byte * 256 GOSUB getbyte: PRINT #2, RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2) IF debug THEN PRINT RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2) loadaddress = loadaddress + byte GOSUB getbyte 'ignore checksum PRINT #2, "******************************************************" PRINT #2, "" codeaddress = loadaddress 'for hexdumps state = 0 END IF IF state = 3 THEN PRINT "reading data block, length ="; byte; " bytes" maxbyte = byte - 1: binstring$ = "" FOR blockbyte = 0 TO maxbyte GOSUB getbyte IF debug THEN IF blockbyte MOD 16 = 0 THEN PRINT RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(blockbyte), 2); ":"; PRINT " "; RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); IF blockbyte MOD 16 = 15 OR blockbyte = maxbyte THEN PRINT END IF IF basicfile AND detokenize AND debug <> 2 THEN 'have to do this one byte at a time GOSUB detokenizestream PRINT #2, streamout$; ELSE IF binarycode = 0 AND debug <> 2 THEN 'unless binary convert to ascii IF byte = 13 THEN PRINT #2, "" 'ignore unprintable characters IF byte >= 32 AND byte <= 126 THEN PRINT #2, CHR$(byte); ELSE 'output a hex dump IF blockbyte MOD 16 = 0 THEN binstring$ = "" PRINT #2, RIGHT$("000" + HEX$(codeaddress), 4); ":"; END IF PRINT #2, " "; RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2); binchar$ = "." IF byte >= 32 AND byte <= 126 THEN binchar$ = CHR$(byte) binstring$ = binstring$ + binchar$ IF blockbyte MOD 16 = 15 OR blockbyte = maxbyte THEN PRINT #2, " "; 'if less than 16 bytes then print 3 spaces for each missing byte IF blockbyte = maxbyte THEN FOR sp = blockbyte MOD 16 + 1 TO 15: PRINT #2, " "; : NEXT sp END IF PRINT #2, binstring$ END IF END IF END IF codeaddress = codeaddress + 1 NEXT blockbyte GOSUB getbyte 'ignore checksum state = 0 END IF IF state = 4 THEN PRINT "reading end of file block" GOSUB getbyte 'ignore checksum state = 0 END IF nextbyte: WEND endprog: CLOSE #1 CLOSE #2 GOTO start 'run again badfilename: PRINT "file not found" 'freebasic considers it an error to close a file that isn't open GOTO start progerr: PRINT "program error" SYSTEM getbyte: 'return one byte in byte from file #1 'has to get 2 bytes from file then split between calls IF odd = 0 THEN GET #1, , inword% 'get 2 bytes iwv = inword% IF iwv < 0 THEN iwv = iwv + 65536 byte = iwv - INT(iwv / 256) * 256 'return low byte odd = 1 ELSE byte = INT(iwv / 256) 'return high byte odd = 0 END IF RETURN detokenizestream: REM input byte in byte, output string in streamout$ REM state controlled by basicstate... '0 = start of line, 1st next line byte (ignore) '1 = 2nd next line byte (ignore) '2 = 1st line number byte '3 = 2nd line number byte '4 = in a basic line, when 00 received print newline and go back to 0 '5 = last byte 255, decode 2nd byte token then go back to 4 streamout$ = "" 'default empty string IF basicstate = 0 THEN basicstate = 1: RETURN 'ignore 1st next-line addr IF basicstate = 1 THEN basicstate = 2: RETURN 'ignore 2nd next-line addr IF basicstate = 2 THEN linenumber = byte * 256: basicstate = 3: RETURN IF basicstate = 3 THEN linenumber = linenumber + byte streamout$ = LTRIM$(STR$(linenumber)) + " " basicstate = 4: RETURN END IF IF basicstate = 4 THEN IF byte = 0 THEN PRINT #2, "": basicstate = 0: RETURN IF byte = 255 THEN basicstate = 5: RETURN IF byte >= 32 AND byte < 127 THEN streamout$ = CHR$(byte): RETURN IF byte = 128 THEN streamout$ = "FOR": RETURN IF byte = 129 THEN streamout$ = "GO": RETURN IF byte = 130 THEN streamout$ = "REM": RETURN IF byte = 131 THEN streamout$ = "'": RETURN IF byte = 132 THEN streamout$ = "ELSE": RETURN IF byte = 133 THEN streamout$ = "IF": RETURN IF byte = 134 THEN streamout$ = "DATA": RETURN IF byte = 135 THEN streamout$ = "PRINT": RETURN IF byte = 136 THEN streamout$ = "ON": RETURN IF byte = 137 THEN streamout$ = "INPUT": RETURN IF byte = 138 THEN streamout$ = "END": RETURN IF byte = 139 THEN streamout$ = "NEXT": RETURN IF byte = 140 THEN streamout$ = "DIM": RETURN IF byte = 141 THEN streamout$ = "READ": RETURN IF byte = 142 THEN streamout$ = "RUN": RETURN IF byte = 143 THEN streamout$ = "RESTORE": RETURN IF byte = 144 THEN streamout$ = "RETURN": RETURN IF byte = 145 THEN streamout$ = "STOP": RETURN IF byte = 146 THEN streamout$ = "POKE": RETURN IF byte = 147 THEN streamout$ = "CONT": RETURN IF byte = 148 THEN streamout$ = "LIST": RETURN IF byte = 149 THEN streamout$ = "CLEAR": RETURN IF byte = 150 THEN streamout$ = "NEW": RETURN IF byte = 151 THEN streamout$ = "CLOAD": RETURN IF byte = 152 THEN streamout$ = "CSAVE": RETURN IF byte = 153 THEN streamout$ = "OPEN": RETURN IF byte = 154 THEN streamout$ = "CLOSE": RETURN IF byte = 155 THEN streamout$ = "LLIST": RETURN IF byte = 156 THEN streamout$ = "SET": RETURN IF byte = 157 THEN streamout$ = "RESET": RETURN IF byte = 158 THEN streamout$ = "CLS": RETURN IF byte = 159 THEN streamout$ = "MOTOR": RETURN IF byte = 160 THEN streamout$ = "SOUND": RETURN IF byte = 161 THEN streamout$ = "AUDIO": RETURN IF byte = 162 THEN streamout$ = "EXEC": RETURN IF byte = 163 THEN streamout$ = "SKIPF": RETURN IF byte = 164 THEN streamout$ = "TAB(": RETURN IF byte = 165 THEN streamout$ = "TO": RETURN IF byte = 166 THEN streamout$ = "SUB": RETURN IF byte = 167 THEN streamout$ = "THEN": RETURN IF byte = 168 THEN streamout$ = "NOT": RETURN IF byte = 169 THEN streamout$ = "STEP": RETURN IF byte = 170 THEN streamout$ = "OFF": RETURN IF byte = 171 THEN streamout$ = "+": RETURN IF byte = 172 THEN streamout$ = "-": RETURN IF byte = 173 THEN streamout$ = "*": RETURN IF byte = 174 THEN streamout$ = "/": RETURN IF byte = 175 THEN streamout$ = "^": RETURN IF byte = 176 THEN streamout$ = "AND": RETURN IF byte = 177 THEN streamout$ = "OR": RETURN IF byte = 178 THEN streamout$ = ">": RETURN IF byte = 179 THEN streamout$ = "=": RETURN IF byte = 180 THEN streamout$ = "<": RETURN IF byte = 181 THEN streamout$ = "DEL": RETURN IF byte = 182 THEN streamout$ = "EDIT": RETURN IF byte = 183 THEN streamout$ = "TRON": RETURN IF byte = 184 THEN streamout$ = "TROFF": RETURN IF byte = 185 THEN streamout$ = "DEF": RETURN IF byte = 186 THEN streamout$ = "LET": RETURN IF byte = 187 THEN streamout$ = "LINE": RETURN IF byte = 188 THEN streamout$ = "PCLS": RETURN IF byte = 189 THEN streamout$ = "PSET": RETURN IF byte = 190 THEN streamout$ = "PRESET": RETURN IF byte = 191 THEN streamout$ = "SCREEN": RETURN IF byte = 192 THEN streamout$ = "PCLEAR": RETURN IF byte = 193 THEN streamout$ = "COLOR": RETURN IF byte = 194 THEN streamout$ = "CIRCLE": RETURN IF byte = 195 THEN streamout$ = "PAINT": RETURN IF byte = 196 THEN streamout$ = "GET": RETURN IF byte = 197 THEN streamout$ = "PUT": RETURN IF byte = 198 THEN streamout$ = "DRAW": RETURN IF byte = 199 THEN streamout$ = "PCOPY": RETURN IF byte = 200 THEN streamout$ = "PMODE": RETURN IF byte = 201 THEN streamout$ = "PLAY": RETURN IF byte = 202 THEN streamout$ = "DLOAD": RETURN IF byte = 203 THEN streamout$ = "RENUM": RETURN IF byte = 204 THEN streamout$ = "FN": RETURN IF byte = 205 THEN streamout$ = "USING": RETURN IF byte = 206 THEN streamout$ = "DIR": RETURN IF byte = 207 THEN streamout$ = "DRIVE": RETURN IF byte = 208 THEN streamout$ = "FIELD": RETURN IF byte = 209 THEN streamout$ = "FILES": RETURN IF byte = 210 THEN streamout$ = "KILL": RETURN IF byte = 211 THEN streamout$ = "LOAD": RETURN IF byte = 212 THEN streamout$ = "LSET": RETURN IF byte = 213 THEN streamout$ = "MERGE": RETURN IF byte = 214 THEN streamout$ = "RENAME": RETURN IF byte = 215 THEN streamout$ = "RSET": RETURN IF byte = 216 THEN streamout$ = "SAVE": RETURN IF byte = 217 THEN streamout$ = "WRITE": RETURN IF byte = 218 THEN streamout$ = "VERIFY": RETURN IF byte = 219 THEN streamout$ = "UNLOAD": RETURN IF byte = 220 THEN streamout$ = "DSKINI": RETURN IF byte = 221 THEN streamout$ = "BACKUP": RETURN IF byte = 222 THEN streamout$ = "COPY": RETURN IF byte = 223 THEN streamout$ = "DSKI$": RETURN IF byte = 224 THEN streamout$ = "DSKO$": RETURN 'unrecognized byte streamout$ = "[" + RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2) + "]": RETURN END IF IF basicstate = 5 THEN IF byte = 128 THEN streamout$ = "SGN" IF byte = 129 THEN streamout$ = "INT" IF byte = 130 THEN streamout$ = "ABS" IF byte = 131 THEN streamout$ = "USR" IF byte = 132 THEN streamout$ = "RND" IF byte = 133 THEN streamout$ = "SIN" IF byte = 134 THEN streamout$ = "PEEK" IF byte = 135 THEN streamout$ = "LEN" IF byte = 136 THEN streamout$ = "STR$" IF byte = 137 THEN streamout$ = "VAL" IF byte = 138 THEN streamout$ = "ASC" IF byte = 139 THEN streamout$ = "CHR$" IF byte = 140 THEN streamout$ = "EOF" IF byte = 141 THEN streamout$ = "JOYSTK" IF byte = 142 THEN streamout$ = "LEFT$" IF byte = 143 THEN streamout$ = "RIGHT$" IF byte = 144 THEN streamout$ = "MID$" IF byte = 145 THEN streamout$ = "POINT" IF byte = 146 THEN streamout$ = "INKEY$" IF byte = 147 THEN streamout$ = "MEM" IF byte = 148 THEN streamout$ = "ATN" IF byte = 149 THEN streamout$ = "COS" IF byte = 150 THEN streamout$ = "TAN" IF byte = 151 THEN streamout$ = "EXP" IF byte = 152 THEN streamout$ = "FIX" IF byte = 153 THEN streamout$ = "LOG" IF byte = 154 THEN streamout$ = "POS" IF byte = 155 THEN streamout$ = "SQR" IF byte = 156 THEN streamout$ = "HEX$" IF byte = 157 THEN streamout$ = "VARPTR" IF byte = 158 THEN streamout$ = "INSTR" IF byte = 159 THEN streamout$ = "TIMER" IF byte = 160 THEN streamout$ = "PPOINT" IF byte = 161 THEN streamout$ = "STRING$" IF byte = 162 THEN streamout$ = "CVN" IF byte = 163 THEN streamout$ = "FREE" IF byte = 164 THEN streamout$ = "LOC" IF byte = 165 THEN streamout$ = "LOF" IF byte = 166 THEN streamout$ = "MKN$" IF byte < 128 OR byte > 166 THEN 'unrecognized 2 byte sequence streamout$ = "[FF][" + RIGHT$("0" + HEX$(byte), 2) + "]" END IF basicstate = 4 'back to normal line parsing END IF RETURN
---------------------- end convcas.bas -------------------------------------------
Oh my.. thank you internet. The detokonizestream: subroutine
could be encoded more compactly but instead I went for the most
straightforward buggyless way, a string of IF statements. The
first section for single-byte tokens returns after each match for
extra speed, but the section for two-byte tokens doesn't return
after each match because it has to switch back to basicstate 4 at
the end.
I originally wrote this program to dump robot saves but soon
extended it to also detokenize BASIC programs and save machine
code programs as hex dumps. Here are some of the outputs...
The hex dumps are boring and big so didn't link any but they look
like this...
******************************************************
NAME:ROBOT TYPE:CODE FORMAT:ASCII SA/LA:3F01 3F01
******************************************************
3F01: 86 02 1F 8B 10 CE 3E FF CE 03 FF 17 13 F2 0F D9 ......>.........
3F11: 0F DA 17 04 17 17 04 03 17 04 39 17 04 48 17 04 ..........9..H..
3F21: 5D 17 03 E6 17 04 1C 17 04 02 17 04 27 16 1B 18 ]...........'...
3F31: 2A 41 4C 50 48 41 0D 52 4F 42 3E 20 3D 52 3A 58 *ALPHA.ROB> =R:X
3F41: 4C 3A 47 52 4F 42 0D 57 41 4C 3E 20 3D 57 3A 54 L:GROB.WAL> =W:T
3F51: 31 3A 47 57 41 4C 0D 53 54 41 52 54 3E 20 43 52 1:GWAL.START> CR
3F61: 4F 42 3A 43 57 41 4C 3A 46 38 3A 3D 3F 3A 54 31 OB:CWAL:F8:=?:T1
3F71: 0D 47 53 54 41 52 54 0D 00 2A 4F 4D 45 47 41 0D .GSTART..*OMEGA.
3F81: 52 4F 42 3E 20 3D 52 3A 58 4D 0D 57 41 4C 3E 20 ROB> =R:XM.WAL>
3F91: 3D 57 3A 54 2D 32 0D 53 54 41 52 54 3E 20 43 52 =W:T-2.START> CR
3FA1: 4F 42 3A 43 57 41 4C 3A 46 38 3A 3D 3F 3A 54 31 OB:CWAL:F8:=?:T1
3FB1: 0D 47 53 54 41 52 54 0D 00 12 43 4F 4C 4F 52 20 .GSTART...COLOR
3FC1: 52 4F 42 4F 54 20 42 41 54 54 4C 45 0E 43 4F 50 ROBOT BATTLE.COP
3FD1: 59 52 49 47 48 54 20 31 39 38 31 19 54 48 45 20 YRIGHT 1981.THE
3FE1: 49 4D 41 47 45 20 50 52 4F 44 55 43 45 52 53 20 IMAGE PRODUCERS
3FF1: 2C 49 4E 43 2E 16 50 52 45 53 53 20 3C 45 4E ,INC..PRESS <EN
4000: 54 45 52 3E 20 54 4F 20 42 45 47 49 4E 10 50 52 TER> TO BEGIN.PR
4010: 45 53 53 20 44 20 46 4F 52 20 44 45 4D 4F 4E 4F ESS D FOR DEMONO
4020: 20 4E 41 4D 45 0E 4C 45 46 54 20 20 20 20 20 52 NAME.LEFT R
4030: 49 47 48 54 12 4E 45 57 20 20 20 20 20 4E 4C 20 IGHT.NEW NL
4040: 20 20 20 20 20 4E 52 12 45 44 49 54 20 20 20 20 NR.EDIT
4050: 45 4C 20 20 20 20 20 20 45 52 12 53 41 56 45 20 EL ER.SAVE
4060: 20 20 20 53 4C 20 20 20 20 20 20 53 52 12 4C 4F SL SR.LO
4070: 41 44 20 20 20 20 4C 4C 20 20 20 20 20 20 4C 52 AD LL LR
4080: 12 43 4F 4D 50 49 4C 45 20 43 4C 20 20 20 20 20 .COMPILE CL
4090: 20 43 52 09 42 41 54 54 4C 45 20 20 42 05 45 4D CR.BATTLE B.EM
40A0: 50 54 59 12 49 4E 53 45 52 54 20 53 4F 55 52 43 PTY.INSERT SOURC
40B0: 45 20 54 41 50 45 0B 52 45 57 49 4E 44 20 54 41 E TAPE.REWIND TA
40C0: 50 45 0A 50 52 45 53 53 20 50 4C 41 59 0A 41 4E PE.PRESS PLAY.AN
40D0: 44 20 52 45 43 4F 52 44 0D 50 52 45 53 53 20 3C D RECORD.PRESS <
40E0: 45 4E 54 45 52 3E 0F 43 4F 4D 50 49 4C 49 4E 47 ENTER>.COMPILING
40F0: 20 52 4F 42 4F 54 0A 53 45 4C 45 43 54 20 4F ROBOT.SELECT O
..... followed by a lot more code.
The maximum length for a ".CAS" record is 255 bytes (not 256) so
in the hex dumps the last line of each record has 15 bytes rather
than 16.. the initial starting address is derived from the load
address. Could have hid the records and flattened to 16 bytes per
line but I didn't want to do that - I want to see where each tape
record ends.
Terry Newton (wtn90125@yahoo.com)